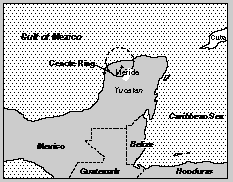

The Chixiclub Crater was found on the Yucatun Peninsula recently. It was dated at 65 million years, the same time the dinosaurs disappeared.
Like my graphic the asteroid came in and hit at about a 30 degree angle moving at roughly 30 km a second and was around 11 km across. The impact threw up billions of tons of dirt to the atmostphere, but more importantly when it broke into the Earth's crust (less than 1 second) it threw up tons of molten rock. The rock that was thrown up faster the 11.2 km/s left our atmosphere, having reached earth's escape speed without acceleration. However, anything less caused it to rain down somewhere on our planet. The re-entry of some of the larger debris could have raised temperatures necessary to "cook" both plants and animals. Much of the molten rock landed closer though, in a 1000 km range. The angle of impact made it direct its primary punch to western-North America. This created huge firestorms which destroyed much of the continent's life.
The acid rain would continue for decades. Its effect would kill plants and animals on land and in the sea. The ocean's acidity content was probably raised high enough to kill much marine life and high enough to kill plankton and other organisms. This would, in effect, kill of any animals that required plankton. etc, etc... It would take hunderds of years for the atmosphere to recover from the blast. Unitl then the temperatures would range from scorching hot days with no protection from UV rays to ice cold nights without the atmosphere to keep heat. The estimated loss from this impact was numbered to about 40% of all life on planet Earth.